Meaning and definition of law -
Law means the rule that is applied to all actions in a derogatory manner. It is the fictitious form of conduct corresponding to which actions are or should be performed. The law is a large body of rules and regulations, based primarily on general principles of justice, fair dealing and convenience, and which are formulated by government bodies to regulate human activities.
In a broader view, law refers to the entire process by which organized societies establish peaceful and orderly relations between people in society through government bodies and workers (legislature, courts, tribunals, law enforcement agencies and officials, codes and preventive institutions, etc.) And there is an effort to implement rules and regulations to maintain.
The concept of law as a guide of human conduct is as old as the existence of a civilized society. The relevance of law to human behavior has become so intimate today that each individual has his or her own concept of self in relation to the nature of law which is undoubtedly influenced by his or her own viewpoint. It is no surprise that finding an agreed definition of the law is the same as the endless journey.
Nature of law , There are differences and differences in the views of legalists regarding the nature, concept, basis and functions of law. The fulfillment of the law as a divinely ordained rule or tradition of customs or as a philosophically created system of principles of written justice for the wise, of the determination and declaration of the nature or eternal or or immovable moral code of things As a body of people's covenants in a politically organized society or as an image of divine reason or as a body of autonomous orders, or as a body of rules invented by human experience, or legislative written rules And be seen as a body of rules developed through judicial decisions or as a body of rules imposed on men and women by the enlightened section of society or in terms of economic and social goals of individuals.
Therefore, law can be defined first by its nature, logic, religion or policies. Secondly - by its sources such as customs, prescriptions or legislation, third - its effect on the life of society, fourth - formal expression or official application of it. , Fifth by the goals they want to achieve.
Definition of law-
However, there is no general definition of law that covers all aspects of law but for general curiosity, some important definitions are as follows.
Aristotle - These (perfect laws) are inherent in human nature and can be derived from human nature.
Austin- Austin says that "law is sovereign - order of the rich".
Setting rules for political juniors by political superiors. In other words, an autonomous member of an independent society or a body of members in which the author of the law is superior.
Peyton- According to Peyton, "law is the body of rules that operate as binding rules in communities and by which regulations are ensured sufficient compliance to enable the binding provision of the rules."
AV Dasi- In the words of AV Dasi "Laws are a reflection of public opinion.
Ihring - Ihring said the law is a kind of guarantee of the conditions of life in society by the power of state control ".
Selmond- According to Selmond, "law is the body of principles recognized and used by the state in the use of justice", that is, the principles accepted and used by the state in the conduct of justice.
Sevine- Law is a subject of subliminal development within the community and can only be understood in its historical perspective. According to Samvinay's balliest theory, law refers to the will of the people.
Rosskoy Pound- " Laws are social controls in a politically organized society through the systematic use of force. "Minimal mind - a tool to fulfill maximum desires in a society with mutilation and decay.
Classification of law-
In order to get a proper and rational law of law, its classification is extremely important. This helps in understanding the principles and logical structure of the legal system. It clarifies the interrelationships of the rules and their effects on each other and helps in concise and systematic set of rules.
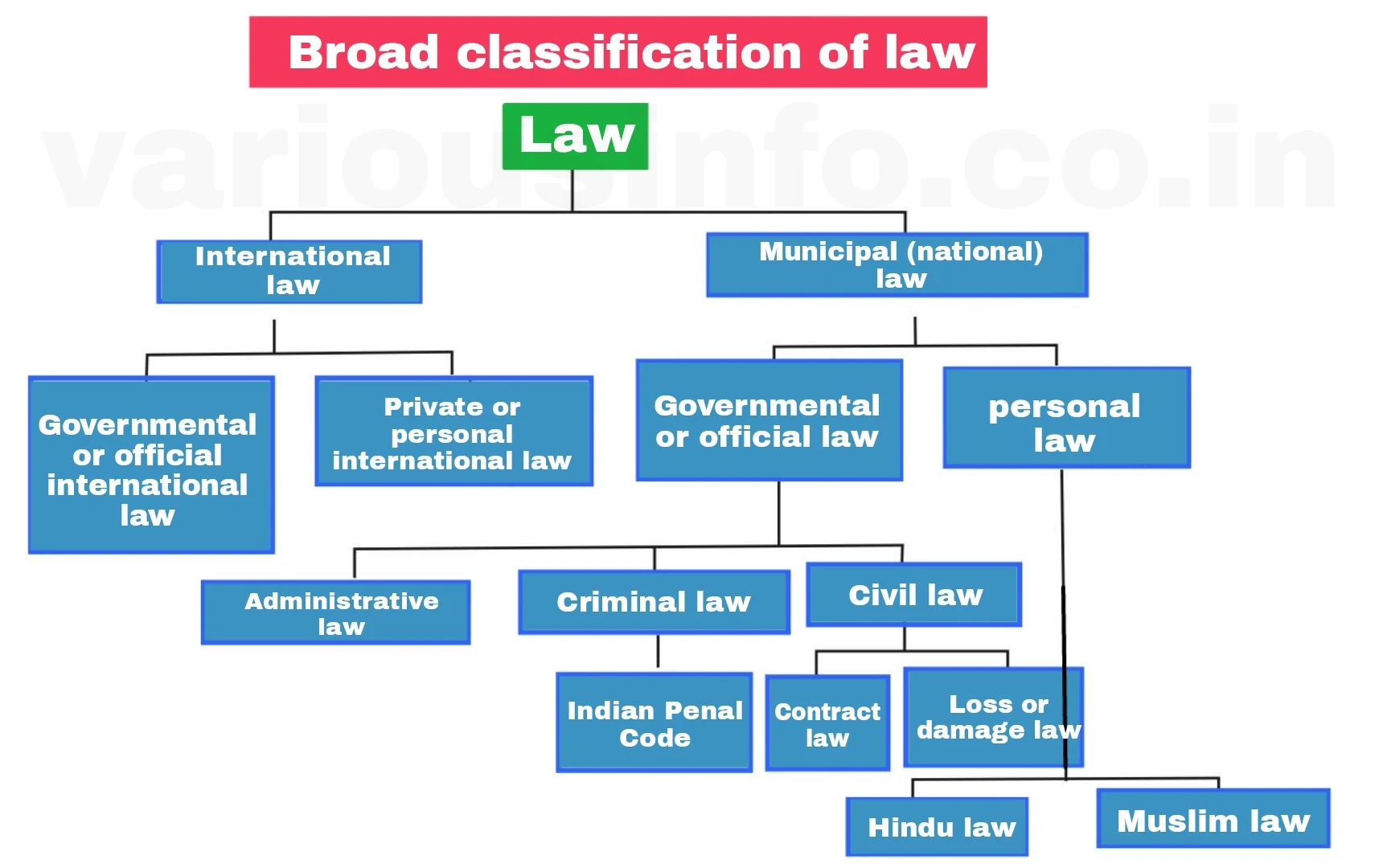
The broad classification of law is as follows-
Broad classification of law Law can be broadly divided into two categories.
1. International law-
International law is that branch of law which includes rules regulating the mutual relations between states or nations. In other words, international rules are a body of customary and traditional rules that are legally binding for civilized nations when dealing with each other. International law is mainly based on treaties between civilized nations. International law can be divided as follows.
(A) Public international law should be the body of rules that govern the conduct and relations of one nation with other nations.
(B) Private international law This refers to the rules and principles according to which cases with foreign elements are dealt with.
For example, if a contract is made between an Indian and a Pakistani citizen in India and it is to be executed in Ceylon. The rights and obligations of the parties are determined by its rules and regulations, they are called 'Private international law'.
2. Municipal or (national) law -
Municipal or national law is a branch of law which is applicable within the state. It can be classified into two categories.
( A )
(i). Constitutional law: Constitutional law is the fundamental or fundamental law of the state. This law determines the nature of the state and the structure of government. It excels the common law of that nation because common law derives authority and powers only from constitutional law.
(ii). Administrative Law: This law is the structure of the powers of administration, the powers and functions, the limits of those powers, the methods and procedures to be followed to exercise their powers, the laws by which their powers are governed and a person against them. Relates to available remedies, when that person's rights are hindered due to their operation.
(iii). Criminal law defines crimes and prescribes punishment for them. Its purpose is to prevent crimes and punish them because in civilized societies, 'crime' is not considered to be a wrongful act against a person but a wrong act against society.
(B) Private law:
This branch of law regulates and governs citizens' mutual relations with each other. This includes personal or personal law such as Hindu law and Muslim law.
In addition to these types of laws, some other types of laws exist, which are as follows.
Natural or moral law:
Natural laws are based on the principle of right and wrong. It incorporates the principles of natural justice.
Customary law :
Customary law refers to a rule or system of rules which are drawn by mutual consent by individuals to regulate their conduct towards each other.
For example, the Indian Contract Act, 1872 deals with the rules relating to contracts or agreements. A customary or customary law, a rule that is followed by humans at the establishment of a practice, is enacted by the state as law, being accepted or accepted by the people.
civil law:
The law promulgated by the state is called civil law. The basis of this law is the force of the state. Civil law is essentially territorial in nature and applies only within the territory of the state concerned.
Sovereign law:
The statutory law deals with the rights and obligations of individuals against the state and prescribes offenses and prescribes penalties for violations of these rights. For example, 511 various offenses in the Indian Penal Code 1860 and these The punishment related to crimes is mentioned.
Procedural law:
It is related to the law and procedure which aims at making the management of justice accessible. It is a mandatory process for enforcement of legal rights and obligations of litigating parties by the court. For example, the Criminal Procedure Code, 1973 (Criminal Procedure Code, 1973) establishes the procedure to be followed to provide punishment to the offender.
Source of law-
To get a complete knowledge of the concept of law, it is extremely important to obtain known sources of law. Source literally means the point from which a concept originates, originates or is created.
Thus, the expression "source of law" refers to the source from which the rules of human conduct originate and derive the legal power of a binding form. Broadly, the source of law can be divided as follows .
1. Customs -
The customs are the oldest and most important source of law. The customs express those principles. Which are themselves created by natural conscience as principles of justice and public utility.
The customs or practices are born of repeated repetition of similar acts and, therefore, reflect customary conduct within a community. Thus uniformity of conduct under similar circumstances is a certification of custom.
Essential elements of customs
In order for law to be valid, traditional methods have to meet certain expectations and some of these are important ones.
A. Antiquity - In order for a custom to be recognized as law, it is necessary to prove that it has existed for a long or long time.
B. Contiunance - The second essential requirement of a method is that it should be in continuous use.
C. Reliability - A method should not be unreliable or non-rational ie it should be device compatible in the application in case of individual cases.
D. Binding feature - The method must have binding power. It should get the support of the common people and it should be a matter of authority.
E. Certainty - A method must be certain. A practice or tradition that was unclear could not be recognized.
F. Conformance - Conduct of use in traditional rules should be consistent.
G. Compatibility with statutory law and public policy - Traditions should be compatible with statutory law and public policy.
2. Judicial prejudice
'Pre-judgment' refers to the set norms or ideals on which future conduct is based. These may be preceding events, judgments or actions pursued under similar circumstances. Judicial pre-judgments are an independent source of law.
Starc Decisis is a Latin word meaning "to comply with a pre-judgment or parable and not to tamper with proven points." The application of full judicial-judgments to render judgments in future cases in lower courts by pre-judgment or adjudicated orderly it shows.
Judicial pre-adjudication or 'stare decisi' has binding power in subsequent cases. It is not a complete judgment which is binding. In other words, every detail given by the judge in the preceding decision is not binding on the future case.
Only that decision of the preceding case determines the reason for the decision of that case or the ratio decidendi is binding as a general principle. The decision base is a general principle used in a decision case. Judgment is given on the basis of rule of law and is of authentic nature.
In addition to the 'decision basis', a decision may also include comments that are not purely relevant to the case before the court. These comments may be based on broad aspects of law and can be an integrated system of judiciary in India. Or may be based on answers to hypothetical questions raised by judges or counsel during the hearing.
These types of comments are 'obiter dicta' and are without any binding authority as till now it is not mandatory for decision making.
3. Legislation :
'Legislation' is a deliberate process of development of law which involves the introduction of rules of human conduct in a prescribed format through the procedure laid down by the agencies designed by the Constitution.
'Vidhan' means the framing of rules of human behavior. The word 'Vidhan' originated from the words Legis and Latum which means to make or establish. Thus, the word "Vidhan" means the making of law.
It is the source of law which includes declaration of legal rules by the competent authority. Legislation includes every expression of the resolution of the legislature. Whether lawmaking or not.
Role of legal system, judiciary, legal professionals and civil society in the enforcement and legalization of law-
At the time when society came into existence, there was hardly any rule to regulate the behavior of the people living in the society. At that time, there was chaos, rustling and chaos.
In the process of development of civilization and society, a need was felt for a system that could regulate human behavior and minimize differences between people on the basis of prescribed principles of justice and fairness.
Many systems were developed for the development and betterment of the society. The role of these arrangements is mentioned below.
Role of law system -
A law system is a set of legal principles and norms for the safe and promotion of people in a society. Thus, it plays an important role by recognizing the rights of the people and prescribing duties and it also provides a way to enforce these rights and duties.
To enforce these rights and duties, the legal system considers the socio-economic and political conditions of the society and sets its own goals and then constructs a set of rules or principles and laws that allow the society to recognize its own Helps in achieving goals.
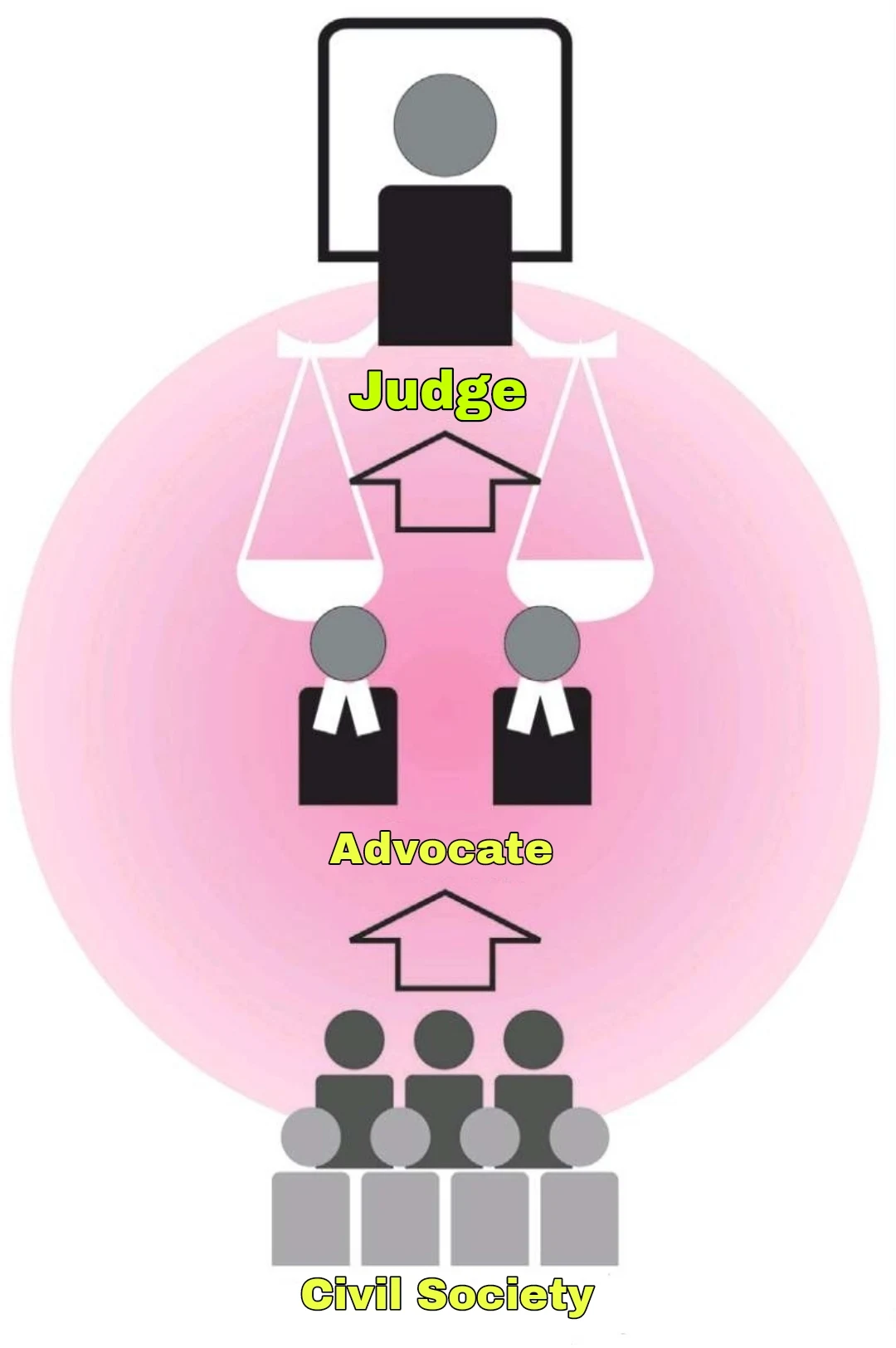
The judge-
Judges who are the defenders of justice are independent of both the executive and the legislature in a democratic system. Therefore, judges are persons who render justice fearlessly or without prejudice. According to proper investigation, give the decision.
Advocate -
Advocates are the key functionaries supporting the judges in the process of delivering justice. Advocates are officers of the court and are part of an independent profession under the Advocates Act, 1961. Without the expert assistance of the lawyers of both sides of the dispute, it becomes difficult for a judge to find out the truth in relation to the disputed facts of the case and interpret justice.
Civil society -
In the public system,"we the people", ie citizens and their elite groups play an important role in good governance. They create pressure groups to attract the attention of the legislature and the government. For example, during the freedom struggle, many movements were launched by Mahatma Gandhi, mass movement against corruption by Anna Hazare. Effective participation of people brings transparency, accountability and reactivity in government.
• Law is a comprehensive body of rules and regulations based on the general principles of justice and equal opportunity to regulate human conduct and behavior.
• In encompassing manner . Law can be classified into international law and municipal (national) law, which can be further subdivided into public and private laws and subsequently into prescriptive and procedural law.
Over time, society has developed a number of means to regulate human conduct and behavior that can minimize differences and chaos in society. The legal system, constitution, bylaws, personnel of law, especially judges, advocates, civil society play an important role in enforcing the rights and obligations of citizens. This will also prevent the prevalence of chaos, differences and corruption in the society.
Various info movie
So friends, how did you like our post! Don't forget to share this with your friends, below Sharing Button Post. Apart from this, if there is any problem in the middle, then don't hesitate to ask in the Comment box. If you want, you can send your question to our email Personal Contact Form as well. We will be happy to assist you. We will keep writing more posts related to this. So do not forget to bookmark (Ctrl + D) our blog “www.variousinfo.co.in” on your mobile or computer and subscribe us now to get all posts in your email. If you like this post, then do not forget to share it with your friends. You can help us reach more people by sharing it on social networking sites like whatsapp, Facebook or Twitter. Thank you !







If you liked the information of this article, then please share your experience by commenting. This is very helpful for us and other readers. Thank you